How China is rewriting the book on human origins
By Jane Qiu,
Nature News
| 07. 12. 2016
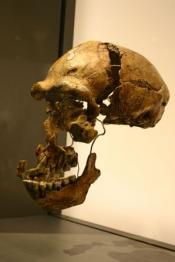
On the outskirts of Beijing, a small limestone mountain named Dragon Bone Hill rises above the surrounding sprawl. Along the northern side, a path leads up to some fenced-off caves that draw 150,000 visitors each year, from schoolchildren to grey-haired pensioners. It was here, in 1929, that researchers discovered a nearly complete ancient skull that they determined was roughly half a million years old. Dubbed Peking Man, it was among the earliest human remains ever uncovered, and it helped to convince many researchers that humanity first evolved in Asia.
Since then, the central importance of Peking Man has faded. Although modern dating methods put the fossil even earlier — at up to 780,000 years old — the specimen has been eclipsed by discoveries in Africa that have yielded much older remains of ancient human relatives. Such finds have cemented Africa's status as the cradle of humanity — the place from which modern humans and their predecessors spread around the globe — and relegated Asia to a kind of evolutionary cul-de-sac.
But the tale of Peking Man has haunted generations of...
Related Articles
By Katherine Long, Ben Foldy, and Lingling Wei, The Wall Street Journal | 12.13.2025
Inside a closed Los Angeles courtroom, something wasn’t right.
Clerks working for family court Judge Amy Pellman were reviewing routine surrogacy petitions when they spotted an unusual pattern: the same name, again and again.
A Chinese billionaire was seeking parental...
By Sarah A. Topol, The New York Times Magazine | 12.14.2025
The women in House 3 rarely had a chance to speak to the women in House 5, but when they did, the things they heard scared them. They didn’t actually know where House 5 was, only that it was huge...
By Frankie Fattorini, Pharmaceutical Technology | 12.02.2025
Próspera, a charter city on Roatán island in Honduras, hosts two biotechs working to combat ageing through gene therapy, as the organisation behind the city advertises its “flexible” regulatory jurisdiction to attract more developers.
In 2021, Minicircle set up a...
By Courtney Withers and Daryna Zadvirna, ABC News | 12.03.2025
Same-sex couples, single people, transgender and intersex West Australians will be able to access assisted reproductive technology (ART) and surrogacy, almost a decade after reforms were first promised.
The landmark legislation, which removes the requirement for people to demonstrate medical...