Aggregated News
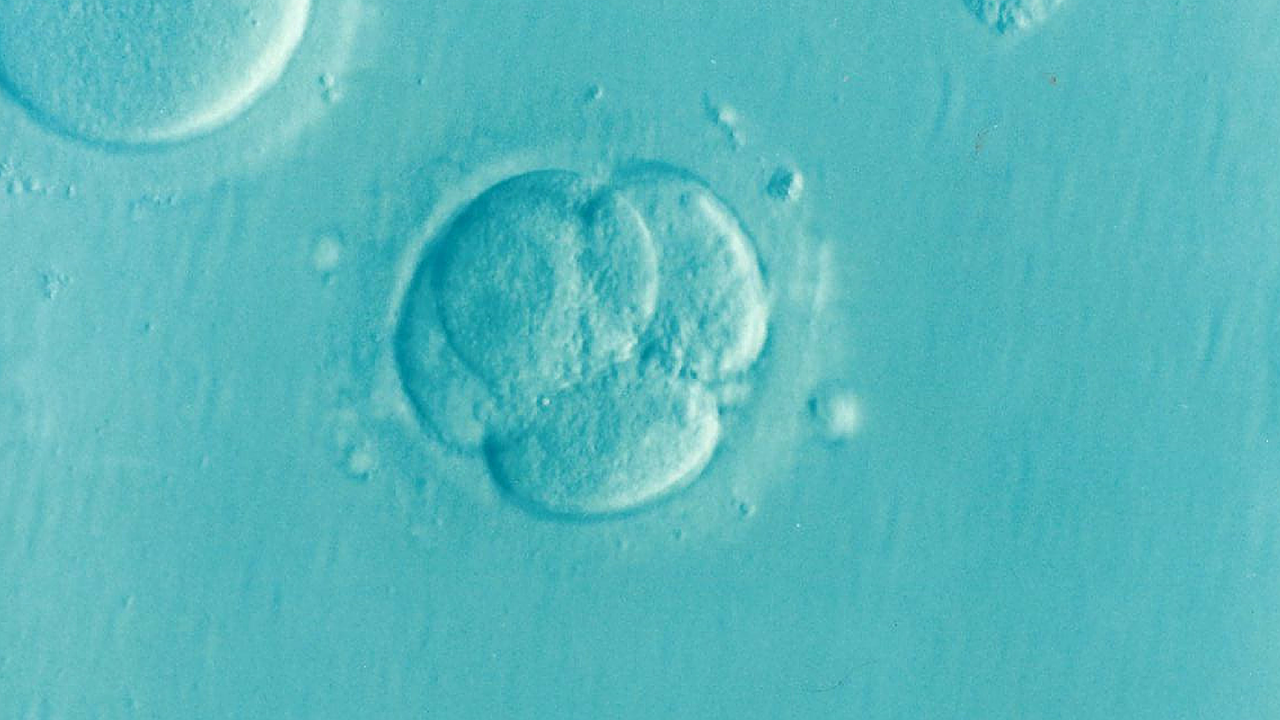
A lab experiment aimed at fixing defective DNA in human embryos shows what can go wrong with this type of gene editing and why leading scientists say it’s too unsafe to try. In more than half of the cases, the editing caused unintended changes, such as loss of an entire chromosome or big chunks of it.
Columbia University researchers describe their work Thursday in the journal Cell. They used CRISPR-Cas9, the same chemical tool that a Chinese scientist used on embryos in 2018 to help make the world’s first gene-edited babies, which landed him in prison and drew international scorn.
The tool lets scientists cut DNA in a precise spot and has profound potential for good — it’s already used to raise better crops and livestock, holds promise for treating diseases, and earned its discoverers a Nobel Prize earlier this month.
But using it on embryos, sperm, or eggs makes changes that can pass to future generations. Several international panels of scientists and ethicists have said it’s too soon to know whether that can be done safely, and the new...



