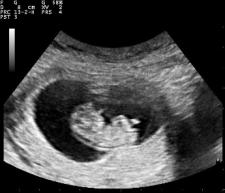
Testing, testing: Prenatal genetic screening
By Joe Gibes,
Trinity International University
| 06. 10. 2016
The June 2016 issue of Obstetrics and Gynecology includes a study of the conversations between patients and “Health Care Providers” about prenatal genetic screening (PGS). The objective of the study was to “assess how obstetric health care providers counsel patients regarding prenatal genetic screening and how these conversations influence patients’ screening decisions.” PGS refers to blood and ultrasound tests performed early in pregnancy to determine whether a fetus is at high risk for various chromosomal anomalies, especially the anomaly that leads to Down syndrome. Several findings of the study are troubling.
First troubling finding: providers’ counseling of patients about PGS lasts an average of 1.5 minutes.
Second troubling finding: False-positive rates of PGS are discussed so rarely that they could not be reliably analyzed in the study. The false-positive rate refers to how often the screening test is wrong when it suggests that an abnormality is present; when a test says the baby has Down syndrome, but the baby in fact does not have Down syndrome, it is a false-positive. The guidelines of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists...
Related Articles
A Review of Exposed by Becky McClain
“Do not get lost in a sea of despair. Be hopeful, be optimistic. Our struggle is not the struggle of a day, a week, a month, or a year, it is the struggle of a lifetime. Never, ever be afraid to make some noise and get in good trouble, necessary trouble.”
— John Lewis
Becky McClain became famous when she successfully sued Pfizer, one of the very largest pharmaceutical and biotech companies. She...
By staff, Japan Times | 12.04.2025
Japan plans to introduce a ban with penalties on implanting a genome-edited fertilized human egg into the womb of a human or another animal amid concerns over "designer babies."
A government expert panel broadly approved a proposal, including the ban...
By Katherine Long, Ben Foldy, and Lingling Wei, The Wall Street Journal | 12.13.2025
Inside a closed Los Angeles courtroom, something wasn’t right.
Clerks working for family court Judge Amy Pellman were reviewing routine surrogacy petitions when they spotted an unusual pattern: the same name, again and again.
A Chinese billionaire was seeking parental...
By Sarah A. Topol, The New York Times Magazine | 12.14.2025
The women in House 3 rarely had a chance to speak to the women in House 5, but when they did, the things they heard scared them. They didn’t actually know where House 5 was, only that it was huge...